ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF NaOH PERCENTAGE ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH OF SISAL FIBER (AGAVE SISALANA) AND POLYURETHANE COMPOSITES USING THE COMPRESSION MOLDING METHOD
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15294/vbwm5m25Keywords:
Composite, Naoh, Tensile Strength, Modulus Elasticity, Sisal FiberAbstract
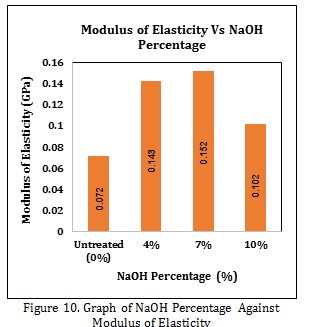
The percentage of NaOH is one of the parameters that greatly affects the sisal fiber composite (Agave Sisalana). The purpose of this study was to observe and analyze the effect of the percentage of NaOH on the tensile strength of sisal fiber composites (Agave Sisalana). The materials used are sisal fiber (Agave Sisalana) and polyurethane resin at various percentages of NaOH, namely without treatment (0%), 4%, 7%, and 10% with soaking time for 2 hours and drying in the sun for a maximum of three days or until the fiber is completely dry. Composite manufacturing was carried out using the compression molding method for 24 hours at a pressure of 50 bar. The tests carried out in this study were tensile tests referring to the ASTM D 638 standard. The percentage of NaOH without treatment (0%) has the lowest maximum tensile value of 6.688 MPa, while the percentage of 7% NaOH has the highest maximum tensile strength value of 11.821 MPa. Then, the percentage of NaOH without treatment (0%) has the lowest maximum elastic modulus value of 0.072 GPa, and the highest maximum elastic modulus value of 0.152 GPa is also found at 7% NaOH percentage.