Potensi Pemberian Bakteri Penghasil IAA (Pseudomonas sp. IAA1 dan Bacillus sp. IAA2) terhadap Perkecambahan Zea mays saccharata Sturt.
Potential of Giving IAA Producing Bacteria (Pseudomonas sp. IAA1 and Bacillus sp. IAA2) on Germination of Zea mays saccharata Sturt.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15294/unnesjlifesci.v14.i1.2214Keywords:
Bacillus sp., Bacteria IAA Producers, Pseudomonas sp.Abstract
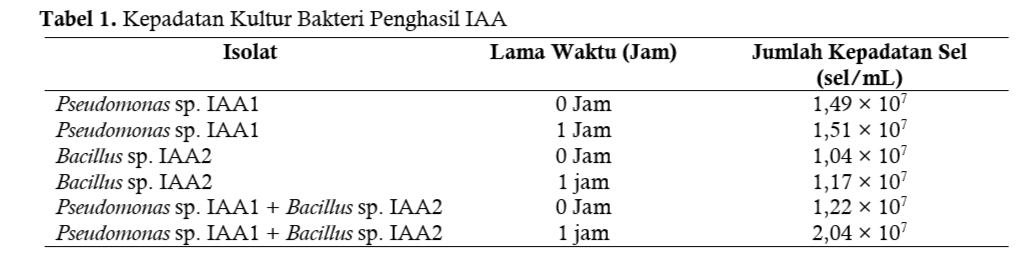
Indigenous peatland bacteria producing indole acetic acid (IAA) hormone function to help in the physiological process of plants during vegetative growth of plants. This study aims to determine the effect of giving IAA-producing bacteria (Pseudomonas sp. IAA1 and Bacillus sp. IAA2) and to determine the best density of IAA-producing bacteria for sweet corn germination (Zea mays saccharata Sturt). This study used a completely randomized design (CRD), with 8 treatment levels and 3 replications. The research data were analyzed using Ms. Excel by finding the average germination time. The results showed that the provision of IAA-producing bacteria had an effect on the germination time of sweet corn plants. The treatment of giving Bacillus sp. IAA2 bacteria with a bacterial density of 1.04 × 107 cells/mL gave the best results in the germination time of sweet corn with an average germination time of 2.00 days, while Pseudomonas sp. IAA1 has a bacterial density of 1.51 × 107 cells/mL and an average sweet corn germination time of 2.25 days. The bacterial consortium of Pseudomonas sp. IAA 1 and Bacillus sp. IAA2 has a bacterial cell density of 2.04 cells/mL and an average sweet corn germination time of 2.30 days. These indigenous bacteria producing IAA can be developed into biofertilizers so that they can replace chemical fertilizers that can harm the environment, especially the soil.
Downloads
References
Alam, H.E.Y., Zulaika, E. (2020). Studi Literatur Potensi Bakteri Endogenik Lahan Gambut Sebagai Biofertilizer Untuk Memperbaiki Nutrisi Lahan. Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS. 9(2), 7-12. https://doi.org/10.12962/j23373520.v9i2.55624
Ardiana, M., & Advinda, L. (2022). The Ability of Fluorescent Pseudomonas to Produce Indole Acetic Acid (IAA). Jurnal Serambi Biologi, 7(1), 59-64, https://doi.org/10.24036/srmb.v7i1.20
Asri C., A, E Zulaika. (2016). Sinergisme Antar Isolat Azotobacter yang Dikonsorsiumkan. Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS. 5(2), 57-59.
Mohod, Satish, G.P. Lakhwat, S.K Deshmukh, R.P. Ugwekar. (2015). Production of Liquid Biofertilizer and its Qualiy Control. International Journal of Emerging Trend in Engineering and Basic Sciences (IJEEBS). 2(3), 158-165.
Murniasih, T., Wibowo, T.J., Putra, M.Y., Untari, F., Maryani, M. (2018). Pengaruh Nutrisi dan Suhu terhadap Selektivitas Potensi Antibakteri yang Berasosiasi dengan Spons. Jurnal Kelautan Tropis. 21(1), 65-70. https://doi.org/10.14710/jkt.v21i1.2084
Pratiwi, E., Satwika, T.D., Akhdiya, A., Agus, F., (2020). Karakterisasi Bakteri Asal Lahan Gambut Jambi dan Potensinya Sebagai Pupuk Hayati. Jurnal Tanah dan Iklim. 44(1), 1-10. 10.21082/jti.v44n1.2020.1-10
Rahmawati, R. (2016). Pengaruh Monosodium Glutamat (MSG) Komersial Terhadap Pertumbuhan Isolat Bakteri Bacillus PL01 dan Pseudomonas PL01 Pada Mineral Salt Medium. [Skripsi. Program Studi Biologi: Institut Teknologi Sepuluh November]
Ryu, C. M., Farag, M. A., Hu, C. H., Reddy, M. S., Wei, H. X., Paré, P. W., & Kloepper, J. W. (2003). Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(8), 4927–4932. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0730845100
Saputri, A., Soesanto, L., Mugiastuti, E., Umayah, A., Sarjito, A. (2020). Eksplorasi dan Uji Virulensi Bakteri Bacillus sp. Endofit Jagung Terhadap Penyakit Busuk Pelepah Jagung. Jurnal Ilmu-Ilmu Pertanian Indonesia. 22(2): 70-78. https://doi.org/10.31186/jipi.22.2.70-78
Sembiring, A., Natalia, L.S. (2021) Isolasi Bakteri Penghasil Asam Indol Asetat (AIA) dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Viabilitas Benih Cabai Merah. Jurnal Agrotek Ummat. 8(1), 27-31. https://doi.org/10.31764/jau.v8i1.4153
Shoda M. 2000. Bacterical control of plant disiase. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 89(6), 512-515. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(00)80049-3
Siallagan, C.R., Sutini, S., Pribadi, D.U., Kusuma, R.M. (2021). Teknologi Budidaya Jagung Manis (Zea mays sacharata Sturt.) Varietas Bonanza dengan Menggunakan Pengaturan Jarak Tanam dan Penggunaan Pupuk NPK, Sains dan Teknologi Pertanian Modern. NST Proceedings. 11-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.11594/nstp.2021.1503
Sofiani M, Djauhari S, Aini, L. Q. (2016). Pengaruh Aplikasi Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) dalam Menghambat Penyakit Rebah Kecambah yang Disebabkan oleh Jamur Sclerotium rolfsii pada Kedelai. Jurnal HPT (Hama Penyakit Tumbuhan). 4(1): 32-38. https://jurnalhpt.ub.ac.id/index.php/jhpt/article/view/226
Un, V., Farida, S., Tito, S.I. (2018). Pengaruh jenis Zat Pengatur Tumbuh terhadap Perkecambahan Benih Cendana (Santalum album Linn.). Indonesian Green Technology Journal. 7(1), 27-34. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.igtj.2018.007.01.05