Kepadatan Bakteri Biofertilizer Cair Air Kelapa Menggunakan Bakteri Pelarut Fosfat (Bacillus spp.) Asal Tanah Gambut Kalimantan Barat
Density of Liquid Biofertilizer Coconut Water Bacteria Using Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus spp.) from West Kalimantan Peat Soil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15294/unnesjlifesci.v14.i1.1673Keywords:
Bacillus cereus, Biofertilizer, Phosphate solubilizing bacteriaAbstract
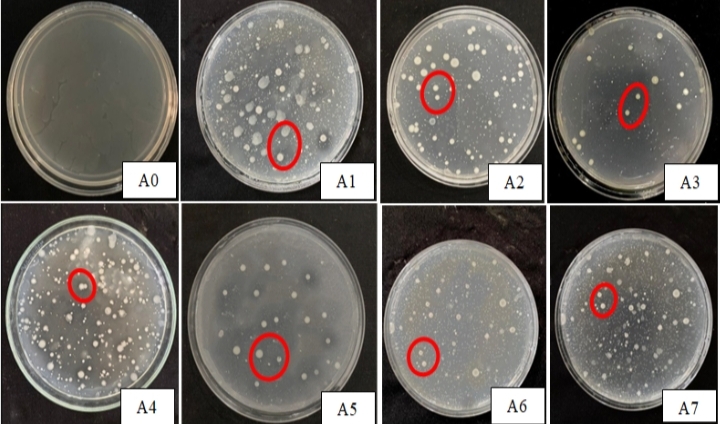
Biofertilizer is an environmentally friendly fertilizer, has a long release time so it can be absorbed by plants long enough, and has enzymatic activities such as binding nitrogen and dissolving phosphate. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria (BPF) can dissolve phosphate that was previously unavailable to become available. This research aims to further examine the potential of BPF isolates from Kalimantan as a liquid biofertilizer agent using coconut water as a medium. The research was conducted for 3 months, from June to August 2023 at the Microbiology Laboratory, Biology Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science Tanjungpura University, Pontianak. This research used a Completely Randomized Design (CRD) with 8 treatments and 3 replications using the Total Plate Count method. The results of the study showed that the highest treatment is a treatment of A4 on day 6 with an average density of 9,4x108 CFU/mL. The BPF which has the highest potential as a biofertilizer is found in treatment A4, the combination bacterial isolates of Bacillus sp1 and Bacillus sp2, supported by the high population treatment of A4 during each storage. Liquid biofertilizers have many advantages compared to solid biofertilizers, including having a higher number of microbial cells, longer shelf life, greater protection against the environment and better effectiveness in the field. This study can provide information on the density of liquid biofertilizer bacteria using environmentally friendly coconut water media for the community by using phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus spp.) from West Kalimantan peat soil.
Downloads
References
Arora, P., Shukla, V., & Singh, G. (2018). Exploring the Role of Glucose in Optimizing in-vitro Growth of Bacterial Isolates under Aluminium Stressed Conditions. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 7(5), 3219– 3223. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.376
Asri, A. C., & Zulaika, E. (2016). Sinergisme Antar Isolat Azotobacter yang Dikonsorsiumkan. Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 5(2), 57-59. http://dx.doi.org/10.12962/j23373520.v5i2.20693
Chen, Q., & Liu, S. (2019). Identification and Characterization of the Phosphate Solubilizing Bacterium Pantoea sp. S32 in Reclamation Soil in Shanxi, China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10(2171). 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02171
Elpawati, Dara, S. D., & Dasumiati. (2015). Optimalisasi Penggunaan Pupuk Kompos dengan Penambahan Effective Microorganism 10 (EM10) pada Produktivitas Tanaman Jagung (Zea mays L.). Al-Kauniyah Jurnal Biologi, 8(2), 77–87. https://doi.org/10.15408/kauniyah.v8i2.2693
Fadlilah, M., & Saputri, F. (2018). Pengaruh Pemberian Air Kelapa Muda Terhadap Tekanan Darah Penderita Hipertensi. Jurnal Ilmiah Multi Science Kesehatan, 9(2), 198–206. http://jurnal.stikes-aisyiyah-palembang.ac.id/index.php/Kep/article/view/132
Fitria, A. N., & Zulaika, E. (2018). Aklimatisasi pH dan Pola Pertumbuhan Bacillus cereus S1 pada Medium MSM Modifikasi. Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 7(2), 39-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.12962/j23373520.v7i2.36788
Fitriatin, B. N., Manurung, D. F., Sofyan, E. T., & Setiawati, M. R. (2020). Compatibility Phosphate Solubility and Phosphatase Activity by Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria. Haya Saudi Journal of Life Science, 5(12), 281-284. https://doi.org/10.36348/sjls.2020.v05i12.003
Gaind, S., & Gaur, A. C. (1991). Thermotolerant Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganism and their Interaction with Mung Bean. Plant and Soil (Historitical Archive), 133(1), 141-149. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011908
Harley P. (2002). Laboratory exercises in microbiology. The Mc Graw Hill Companies
Simbolon, K. (2008). Pengaruh Persentase Ragi Tape dan Lama Fermentasi Terhadap Mutu Tape Ubi Jalar, [Skripsi Sarjana, Universitas Sumatera Utara]. https://repositori.usu.ac.id/handle/123456789/52229
Lestari, N. W., Budiharjo, A., dan Pangastuti, A. (2016). Bakteri Heterotrof Aerobic Asal Saluran Pencernaan Ikan Sidat (Anguilla bicolor bicolor) dan Potensinya Sebagai Probiotik. Jurnal Bioteknologi, 13(1), 9-17. https://doi.org/10.13057/biotek/c130102
Neneng, L., Jagau, Y., & Gunawan, E. Y. (2018). Pengaruh Komposisi Biofertilizer Cair Terhadap Pertumbuhan Tanaman Kedelai di Lahan Gambut. Jurnal Agripeat, 19(1), 30-36. https://doi.org/10.36873/agp.v19i01
Oksana, Irfan, M., Fianiray, A. R. dan Zam, S.I. (2020). Isolasi dan Identifikasi Bakteri Pelarut Fosfat pada Tanah Kecamatan Rumbai, Pekanbaru. Agrotechnology Research, 4(1), 22-25, https://doi.org/10.20961/agrotechresj.v4i1.36063.
Peraturan Menteri Pertanian Nomor 70/Permentan/SR.140/10/2011. Pupuk Organik, Pupuk Hayati dan Pembenah Tanah. Lampiran I, Persyaratan Teknik Minimal Pupuk Organik Padat
Saeid, A., Prochownik, E., & Iwanek, J. D. (2018). Phosphorus Solubilization by Bacillus Species. Molecules, 23(11), 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112897
Salaki, C.L. (2011). Isolasi dan Karakteristik Bakteri Indigeneous (Bacillus cereus Frank.) sebagai Agen Pengendalian Hayati Terhadap Hama Kubis, Jurnal Eugenia. 17 (1), 10-15.
Sarjiya, A., & Dwi, A. (2011). Effects of Biofertilizer Containing Microbial of N-fixer, P Solubilizer and Plant Growth Factor Producer on Cabbage (Brassica oleraceae Var. Capitata) Growth and Soil Enzymatic Activities: A greenhouse Trial. Berkala Penelitian Hayati, 16(2), 149-153 DOI: 10.23869/301 Cibinong: Research Center for Biology – Indonesian Institut of Science.
Saraswati, D. (2014). Pengaruh Konsentrasi Air Kelapa Muda Terhadap Pertumbuhan Saccharomyces cereviceae. [Repositori, Universitas Gorontalo].
Selvi, K. B., Paul, J. J. A., Vijaya, V., & Saraswathi, K. (2017). Analyzing the Efficacy of Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms by Enrichment Culture Techniques. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Journal, 3(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.21767/2471-8084.100029
Setiawati, M. R., Fitriatin, B. N., & Herdiyantoro, D. (2014). Karakterisasi Isolat Bakteri Pelarut Fosfat untuk Meningkatkan Ketersedian P pada Media Kultur Cair Tanaman Jagung (Zea mays L.). Bionatura, 16(1),30-34
Sinaga, D. (2010). Pembuatan Pupuk Cair dari Sampah Organik dengan Menggunakan Boisca sebagai Starter. [Skripsi, Universitas Sumatera Utara]. https://repositori.usu.ac.id/handle/ 123456789/59252
Stephen, J., Shabanamol, S., Kallapurakal, R. & Jisha, S. (2015). Growth Enhancement of Rice by Phosphate Solubilizing Gluconacetobacter sp. and Burkholderia sp. under Greenhouse Conditions. Biotechnol, 5:831-83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-015-0286-5
Sylvia, D. M., Fuhrmann, J.J., Hartel, P.G, & Zuberer, D.A. (2005). Principles and applications of soil microbiology. Second Edition. Upper Saddle River
Wahyu, L., Tetty Marta L, & Atria M. (2011). Kemampuan Bakteri Pelarut Fosfat Isolat Asal Sei Garo dalam Penyediaan Fosfat Terlarut dan Serapannya pada Tanaman Kedelai. Biospesies, 4(2): 1-5. https://doi.org/10.22437/biospecies.v4i2.708
Wijayati, N., Christina, A. & Mulyati, S. (2014). Transformasi α-pinena dengan Bakteri Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 25923. Biosaintifika, 6(1), 24-28. https://doi.org/10.15294/ biosaintifika.v6i1.2931
Yelti, S.N., Zul, D. & Fibriarti, B. N. (2014). Formulasi Biofertilizer Cair Menggunakan Bakteri Pelarut Fosfat Indigenus Asal Tanah Gambut Riau. JOM FMIPA, 1(2), 651-662
Yulensri, Noveri, Arneti. 2018. Pengembangan Bakteri Pelarut Fosfat, Pengikat Nitrogen, Agen Hayati Asal Mikroorganisme Lokal Sebagai Biofertilizer dan Biopestisida untuk Meningkatkan Produktivitas Hasil Padi di Lahan Organik. [Laporan Penelitian. Politeknik Pertanian Negeri Payakumbuh]